Heart Blocks - AV Blocks Explained Clearly
First, Second and Third-Degree AV Blocks explained in 5 min - It's mind-boggling how easy it is!
This lesson includes an animated video lecture, downloadable images, quiz questions and a PDF
The heart electrical signals are initiated in its natural pacemaker - the sinoatrial node, or SA node, and travel through the atria to reach the atrioventricular node, or AV node. The AV node is the gateway to the ventricles. The AV node passes the signals onto the bundle of His. This bundle is then divided into left and right bundle branches which conduct the impulses toward the apex of the heart. The signals are then passed onto fascicular branches, and spread through millions of Purkinje fibers over the ventricular myocardium. 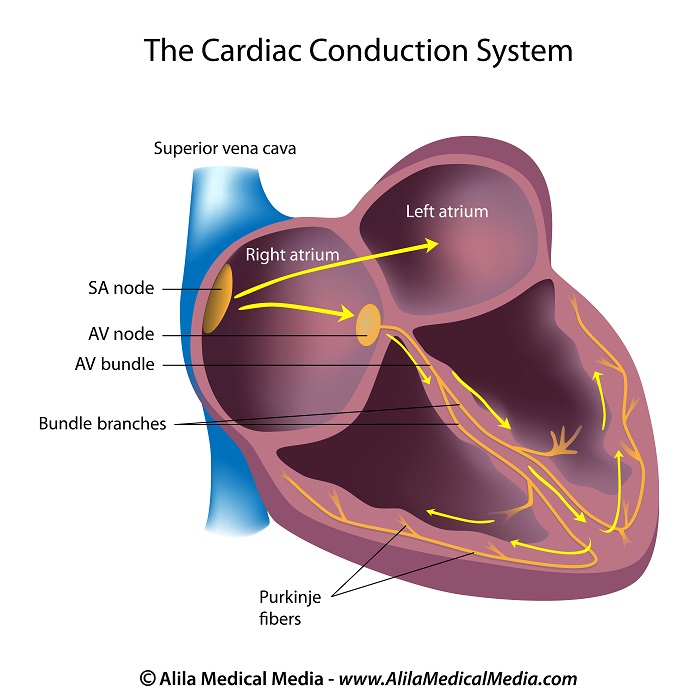
Heart block is a group of diseases characterized by presence of an obstruction, or a “block” in the heart electrical pathway. A block may slow down the conduction of electrical impulses, or, in more severe cases, completely stop them. Heart blocks are classified by location where the blockage occurs. Accordingly, there are: SA nodal blocks, AV nodal blocks, intra-Hisian blocks, bundle branch blocks and fascicular blocks.
Of these, AV nodal blocks, or AV blocks, are most clinically significant. In fact, very commonly, the term “heart block “, if not specified otherwise, is used to describe AV blocks. In AV blocks, the electrical signals are slow to reach the ventricles, or completely interrupted before reaching the ventricles.
Subscribe to one of the courses below to continue!
This content is available within the following courses:

Our Signature Animated Videos on Electrocardiography: 25 animations, plus downloadable PDFs, downloadable images, and quizzes.

Our Signature Animated Videos on Electrocardiography: 25 animations, plus downloadable PDFs, downloadable images, and quizzes.