Anticoagulants Explained Clearly
Mechanisms of Action of Heparin, LMW Heparin, Fondaparinux, Vitamin K Antagonists (Warfarin) and Direct Oral Anticoagulants (DOAs) Explained in 6 minutes.
This lesson includes an animated video lecture, downloadable images, quiz questions and a PDF
Anticoagulants are medications that reduce blood clotting, or coagulation. They are used to treat and prevent unwanted blood clot formation in conditions such as atrial fibrillation, deep vein thrombosis, acute coronary syndrome, and in patients with a prosthetic heart valve. Anticoagulants are also used to prevent excess coagulation during surgery and dialysis.
Coagulation is critical for the control of bleeding, which has 4 stages:
Fibrin is the final product of the coagulation cascade - a multi-step chain reaction where one clotting factor activates the next. The 2 activation pathways, extrinsic and intrinsic, converge to produce thrombin and ultimately fibrin. Thrombin has a central role: it cleaves fibrinogen to generate fibrin, it further activates platelets, and initiates a positive feedback loop that is essential for clot propagation. 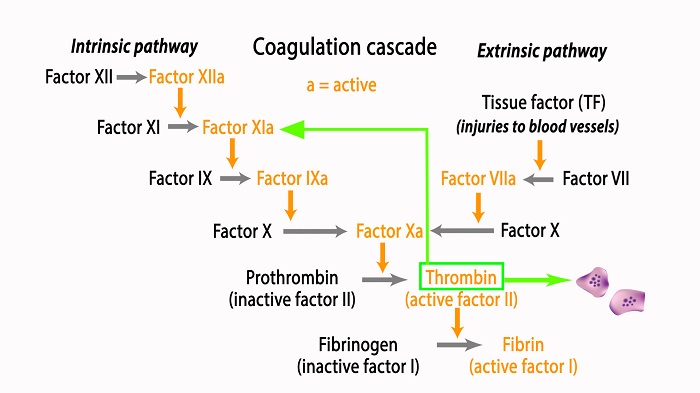
Subscribe to one of the courses below to continue!
This content is available within the following courses:

Basic Fundamentals of Cardiology: 40 animations, plus downloadable PDFs, downloadable images, and quizzes.

Basic Fundamentals of Cardiology: 40 animations, plus downloadable PDFs, downloadable images, and quizzes.