The 12 Lead ECG System Explained Clearly
12 Lead ECG System explained in 4 min - It's mind-boggling how easy it is!
This lesson includes an animated video lecture, downloadable images, quiz questions and a PDF
Electrical activities of the heart can be picked up on the skin via electrodes. An ECG machine records these activities and displays them graphically. The graphs show the heart’s overall electrical potential, or voltage, as it changes over time during a cardiac cycle.
The 12 leads of the ECG represent 12 electrical views of the heart from 12 different angles. 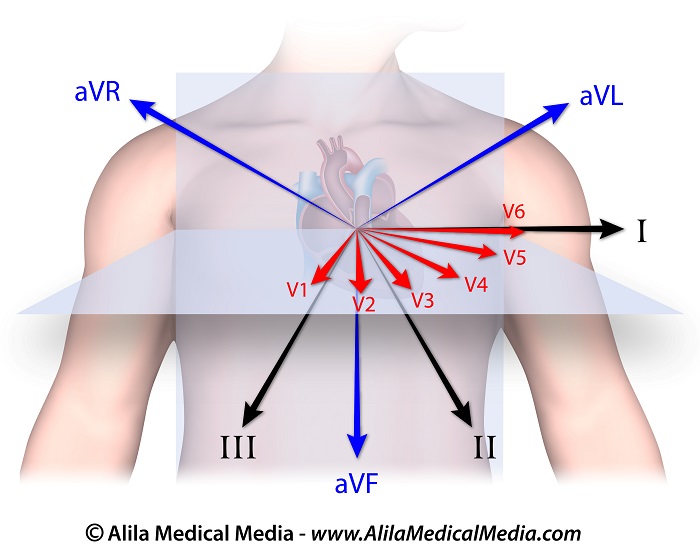 The 12 leads
The 12 leads
Leads and electrodes are different things! Electrodes are those patches (that you can see), used to measure electrical voltage - You need 2 electrodes to measure the electrical potential between the 2 points. Leads are measurements obtained by the electrodes.
The conventional 12-lead procedure involves attaching 10 electrodes to the body: one to each limb and six across the chest.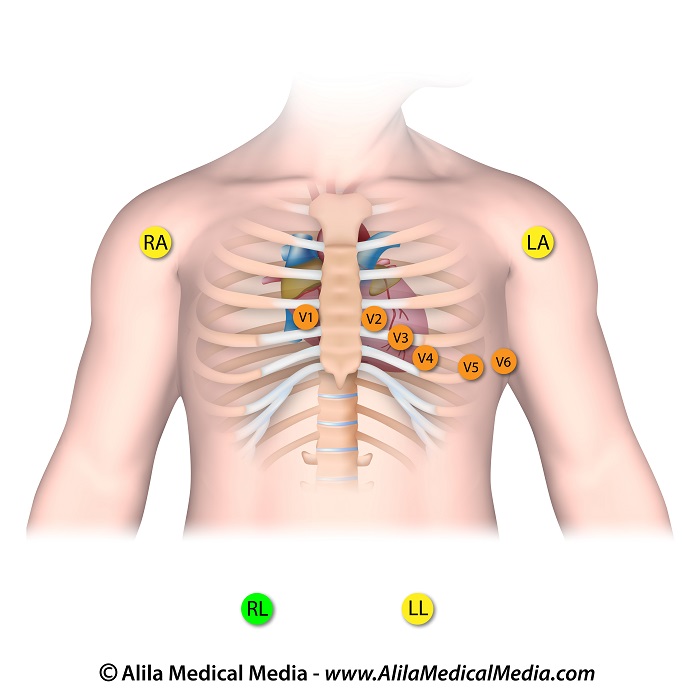 The 10 electrodes
The 10 electrodes
There are 6 limb leads and 6 chest leads.
The 6 limb leads look at the heart in a vertical plane and are obtained from three electrodes attached to the right arm, left arm, and left leg. The electrode on the right leg is an earth electrode.
The measurement of a voltage requires 2 poles: negative and positive. The ECG machine uses the negative pole as zero reference. Thus, the position of the positive pole is the “point of view”, and the line connecting the 2 poles is the “line of sight”.
Subscribe to one of the courses below to continue!
This content is available within the following courses:

Our Signature Animated Videos on Electrocardiography: 25 animations, plus downloadable PDFs, downloadable images, and quizzes.

Our Signature Animated Videos on Electrocardiography: 25 animations, plus downloadable PDFs, downloadable images, and quizzes.