ECG Made Easy - QRS Transitional Zone Explained Clearly
The QRS transitional zone explained in 4 min - It's mind-boggling how easy it is!
This lesson includes an animated video lecture, downloadable images, quiz questions and a PDF
The chest leads look at the heart in a horizontal plane. V1 has the rightmost view, and V6 - the leftmost. 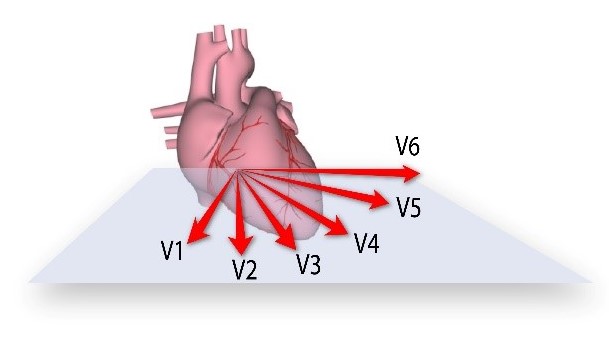
The QRS complex represents depolarization of the ventricles starting with the inter-ventricular septum.
In normal conduction, depolarization of the septum is initiated from the left bundle going to the right, toward V1 and away from V6. This results in a small positive deflection in V1 and a negative deflection in V6.
The signals then move both directions to the two ventricles, but as the left ventricle is usually much larger, the net movement is to the left, away from V1, toward V6. This corresponds to a negative wave in V1 and a positive wave in V6.
Thus, the QRS complex starts as predominantly negative in V1, and ends as predominantly positive in V6.
Somewhere in between, usually from V3 to V4, it is isoelectric, with similar positive and negative deflections. This is known as the transitional zone.
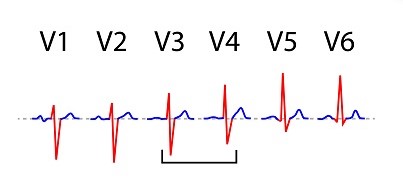
In addition, there is a gradual increase in amplitude of R wave from V1 to V5. This is known as R wave progression.
Subscribe to one of the courses below to continue!
This content is available within the following courses:

Our Signature Animated Videos on Electrocardiography: 25 animations, plus downloadable PDFs, downloadable images, and quizzes.

Our Signature Animated Videos on Electrocardiography: 25 animations, plus downloadable PDFs, downloadable images, and quizzes.